
English | 中文

GoldenBee Research on CSR Reports of Foreign-invested Enterprises in China
source:goldencsr date:2016-09-01 14:34:14The foreign-invested enterprise is the enterprise invested by both Chinese investors and foreign investors or only by foreign investors and set up in China in accordance with the law of the People’s Republic of China.
As of October 31, 2015, we collected 98 CSR reports released by foreign-invested enterprises through their submission, downloading from their website, network searching and other channels, with year-on-year growth of 104.2%. We evaluated them in accordance with GoldenBee CSR Report Evaluation System 2015. Besides, we gave a general description of these reports, comparing, analyzing and evaluating their overall quality and summarizing their characteristics on the basis of reporting parameters and in connection with our experience in preparing and consulting of CSR reports. On this basis, we made relevant recommendation.
The overview of the CSR reports of foreign-invested enterprises: the number has increased, but the proportion has dropped
In recent years, the reports released by foreign-invested enterprises have increased in the number. However, their proportion among the reports released in China has dropped. Part of the reason is that Chinese enterprises have increasingly focused on information disclosure and transparency through the reports and the foreign-invested enterprises, especially the European enterprises, have explored a comprehensive report by combining corporate social responsibility report with annual report.
32 32 enterprises who release reports headquarter in Japan, making up the nearly one third--the largest part of the samples.
56.6% 56.6% reports are environmental reports,showing a higher proportion than that of CSR reports and sustainability reports among the samples,which indicates that the environment is of particular concern for foreign-invested enterprises.
34.3% Over one third enterprise release the reports for five times or above and most of their reports are released successively. The regular release system has been established gradually.
47.5% Nearly half of the reports with 11-30 pages, and about 29.3% reports with more than 51 pages.it is needed to enrich the content of the reports.
57.6% Nearly six out of ten reports come from the branches in China,indicating a further communication between foreign-invested enterprises and Chinese stakeholders.
85.9% About 85.9% enterprises are in manufacturing field among the samples. They show a higher initiative to release the report with special focus on the impact on environment during the production process.
GRI Sustainability Reporting Guidelines from GRI is the document that has been referred to most and 27.3% reports use it as the reporting framework. Meanwhile, nearly one third enterprises use multi-standards as the reporting framework.
19.2% Nearly 20 reports in the samples accept the third-party assurance, accounting for 19.2 %, which shows an increase proportion among the total reports
The CSR reports of foreign-invested enterprises are generally in the development stage.
On the basis of scores, we divided these reports into five levels: infancy, development, upswing, excellence, and outstanding. The average score of the reports is 45.71, in the development stage. The reports in outstanding stage are less than 10 %; about 25 % reports in excellence and upswing stage. A relatively high quantity of reports are still in the development stage and most of the reports are in the infancy stage with the proportion of more than 40%.
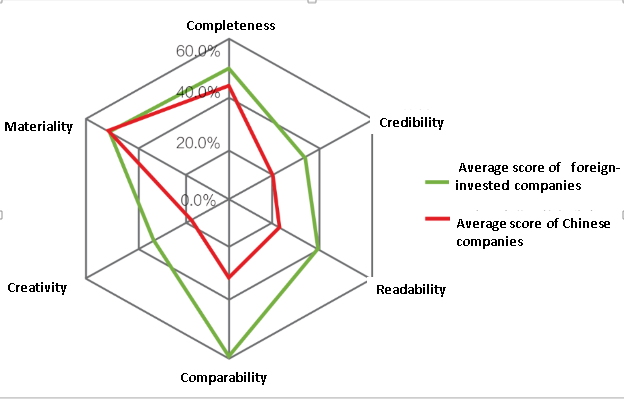
The CSR Reports of foreign-invested enterprises have significant advantages in comparability, readability, innovation, credibility and creativity and the quality is higher than that of the reports in China on the whole. Especially, the comparability of these reports highly stand out and the comparison of performance between different years and different industries are also highly valued.
Our Findings:
Finding I: The reports based on regional headquarters have higher quality than those based on a single enterprise
When the foreign-invested enterprises enter China, they often set up one or more companies according to the service attribute. Then, the expansion of business entities in China will promote the enterprise to build regional headquarters. Since the regional headquarters have strengthened the communication function and keep a more uniform pace with the Group headquarter in strategy and management, the reports based on regional headquarters generally have higher quality. In the sample, the average score of the single enterprises is 35.3 and that of the regional headquarters is 67.9. For example, the score of Samsung China’s report comes out top among all the reports of foreign-invested enterprises. However, the average score of the reports of three Samsung subsidiaries in China is less than half of the score of Samsung China's report.
Finding II: Actively using the latest guideline from Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
While disclosing the social responsibility information, foreign-invested enterprises focus on the reference and application of the latest international trend and standards. In the sample, 18.9% foreign-invested enterprises use Sustainability Reporting Guidelines (G4) as the reporting framework, the latest reporting guideline from GRI. However, this proportion of regional headquarters is 50%. For instance, a series of enterprises, such as Eton China, order the issues and define the core content of the report that can be disclosed according to the importance of issues for external stakeholders and successful business operation of enterprises.
Finding III: Starting to set up localized system of social responsibility management
Basically, the headquarters of foreign-invested enterprises that have released reports all have definite concepts of social responsibility and management strategy. Most foreign-invested enterprises carry out some localized programs within the management framework of their headquarters. With the development of business in China and the systematization of corporate social responsibility management, a few foreign-invested enterprises, advanced in the field of social responsibility, have developed the plan or management strategy in line with the sustainable development of enterprises in China by combining the social responsibility framework of headquarters with Chinese local characteristics. For example, Canon China makes 2020 Sustainability Plan and Sony China defines the management model of corporate social responsibility.
Finding IV: Valuing the disclosure of the issues related to environmental management and social responsibility management of supplier
Relying on the systematic environmental management and supplier management of parent company, foreign-invested enterprises, combined with the real situation of China, set up systematized environmental management and supplier management system. In the sample, more than 80% enterprises are manufacturing enterprises and they especially value their impact on environment and the sustainable development of supply chains. Therefore, their coverage rates of issues on environmental management and supplier management in their reports are more than two times of those reported by any other enterprise. However, the coverage rates of issues on employees and the government are less than the average coverage rates of those of all enterprises in the sample. This is because foreign-invested enterprises think that the issues on compliance with laws and regulations, paying taxes and participating in social security are the basic duties of enterprises. Besides, the specific appeals from employees in Chinese business environment, such as labor union and employee assistance, have not formed issue management.
Finding V: Constantly improving reading experience by the content and format innovation
The foreign-invested enterprises which released reports for years keep in step with the latest international and domestic standards and keep innovation to realize a better communication effectiveness. They are also good at giving readers a fresh feeling by telling stories. For example, Fuji Xerox China uses personification in the feature chapter to tell the story about the whole life cycle of the product and vividly reflects its social responsibility management that has integrated into the value chains.
Our Suggestions:
Suggestion I: Actively using Chinese National Social Responsibility Standards to improve the social responsibility reporting
With the release of Chinese National Social Responsibility Standards, namely Guidance on Social Responsibility GB/T 36000-2015, Guidance on Social Responsibility Reporting GB/T 36001-2015, and Guidance on Classifying Social Responsibility Performance GB/T 36002-2015, The foreign-invested enterprises, when disclosing the localized social responsibility information , need to actively respond to the requirement from the stakeholders, and pay more attention to the pertinence and adaptability under Chinese environment. For example, they should pay more attention to and get close to the latest requirements of China's relevant laws and regulations, and follow the principles of completeness, comprehensiveness, objectivity and accuracy, clear response, timeliness and comparability, readability, and availability in information disclosure, to further strengthen the understanding and support from stakeholders in China.
Suggestion II: Properly disclosing the methods and approaches of the localized social responsibility management
Many foreign-invested enterprises have complete social responsibility management system and propelling methods in the headquarters. However, in China, their reports often lack the description of localized implementation. This makes it difficult for the stakeholders who are interested in local social responsibility management to comprehensively understand and learn the feasible measures. Since the latest reporting guidelines G4 from GRI pays more attention to the disclosure of management methods, foreign-invested enterprises can present the related mechanism and process in detail and display the logical thinking of management while introducing the whole system of the headquarter.
Suggestion III: Using diversified media and channels to communicate with stakeholders
rapid development of mobile internet brings clear features of mass communication, such as paperless, picture-reading and fragmentization. Foreign-invested enterprises need to communicate with the stakeholders in a more innovative and appropriate way, such as H5 Micro Reports on WeChat and small CSR videos. Moreover, as the most important internal stakeholder, Employees are the key to the implementation of the social responsibility concept and strategy and, it also a tool and an approach to disseminate the training based on reports or the CSR Monthly/Quarterly within the enterprise.
Suggestion IV: actively participating in all kinds of communication platforms.
Most foreign-invested enterprises have certain limitations in communication in the business and industrial fields. The corporate social responsibility in China has made great progress and shows“Five-in-one for Joint Promotion” pattern, which means that government, sector, enterprise, society and international cooperation have formed five forces in promoting CSR development. Foreign-invested companies need to know the development trend of the corporate social responsibility in China, and also need to have dialogue with Chinese companies to learn the advanced methods, patterns and experiences from each other, and contribute to the sustainable development of society in China by sharing their own experiences.