
English | 中文

GoldenBee Research on CSR Reporting in China 2018 released
source:goldencsr date:2018-12-27 15:27:57
As a traditional module and highlight of the International Conference on CSR Reporting in China, GoldenBee Research on Corporate Social Responsibility Reporting in China 2018 (hereinafter referred to as “the Research Report”), was released during the 11th International Conference on CSR Reporting in China on December 6.
Following the GoldenBee research methodology in 2017, GoldenBee CSR Consulting systematically analyzed 1,579 CSR reports, and compiled the Research Report.
From 2001 to 2018, the number of social responsibility reports issued by enterprises in China increased year by year. From January 1 to October 31, 2018, a total of 1,676 social responsibility reports were released, increasing by 8.5% year on year. The reporting enterprises are mainly from manufacturing, financial and insurance, information technology (IT), power, coal, water and gas production and supply, social services, storage and transport industry, etc. The listed enterprises, state-owned enterprises (SOEs) and state-controlled enterprises are still the main forces in CSR reporting.
The GoldenBee “Three Excellence” theoretical model of CSR reporting, namely excellent basic information disclosure, excellent response to core content, and excellent compliance with basic principles, was applied in the Research Report. Based on a large number of text and data analysis, GoldenBee deeply analyzed the characteristics of CSR reports released in China in 2018, and offered specific suggestions on the CSR reporting in China to provide references for enterprises to compile high-quality CSR reports.
Ten characteristics:
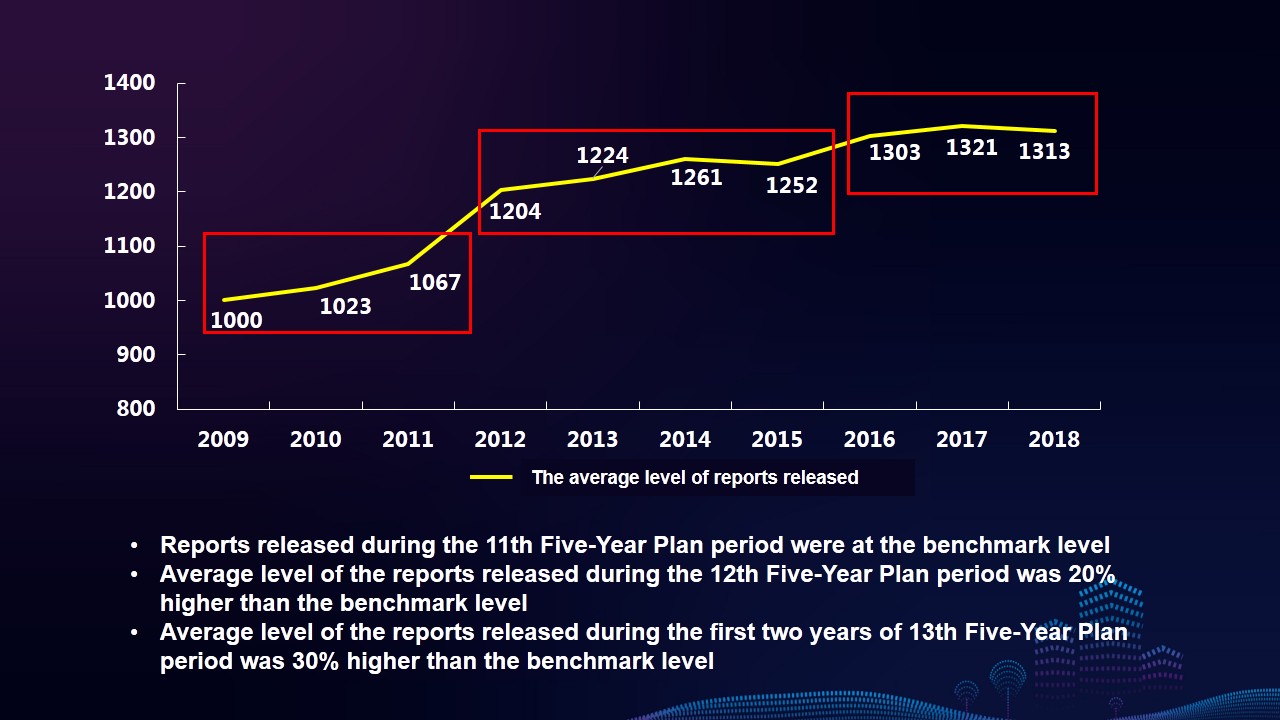
Characteristics 1: The overall level of reports shows a stepwise upward trend, but the proportion of reports in “good” rating and above decreases year on year.
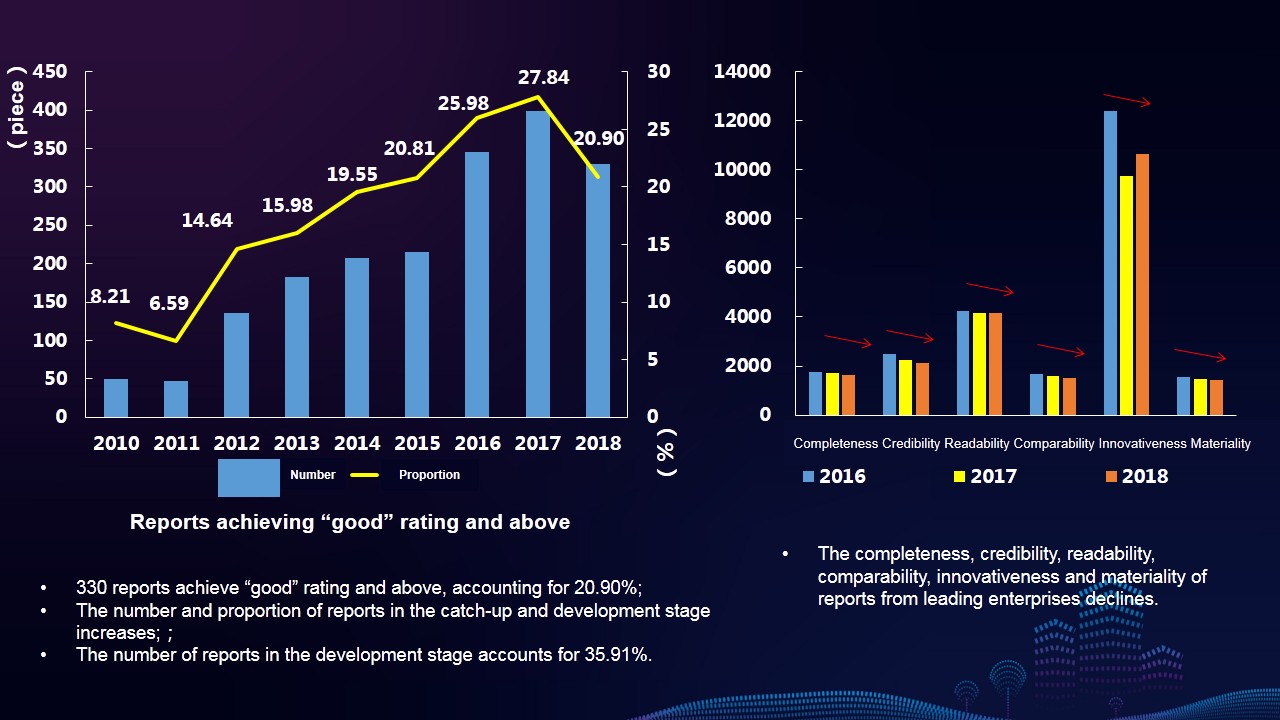
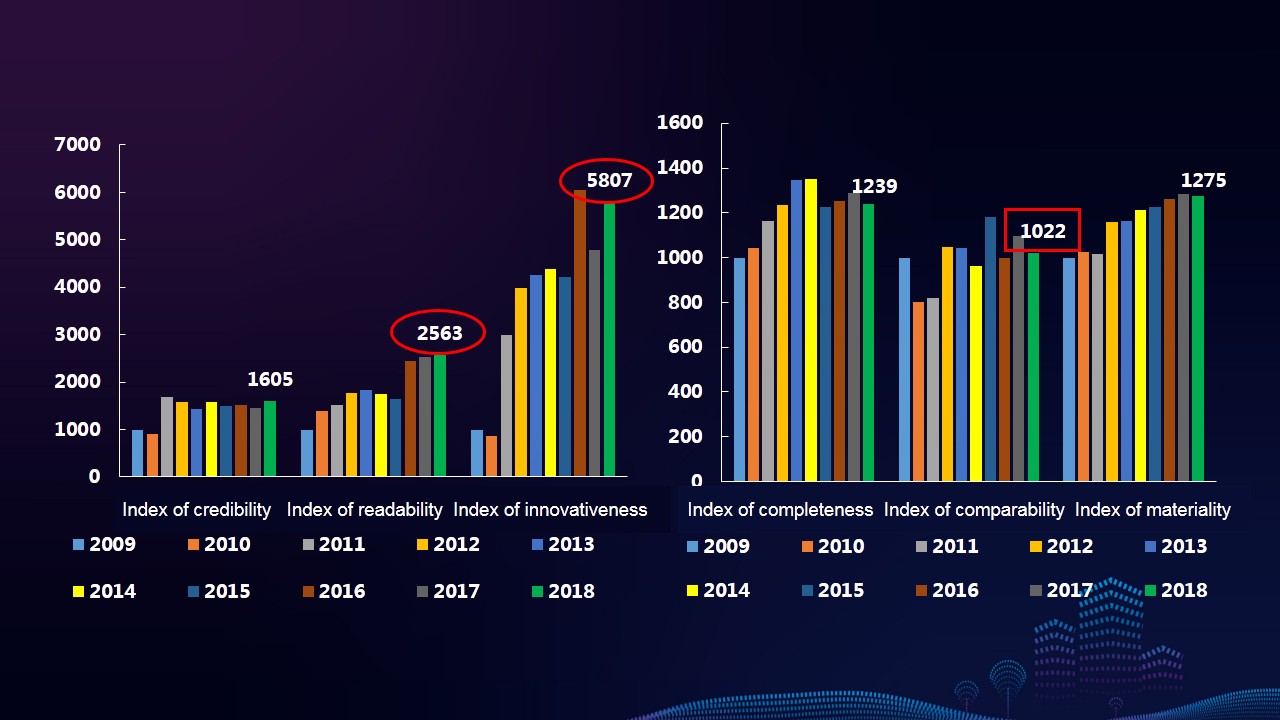
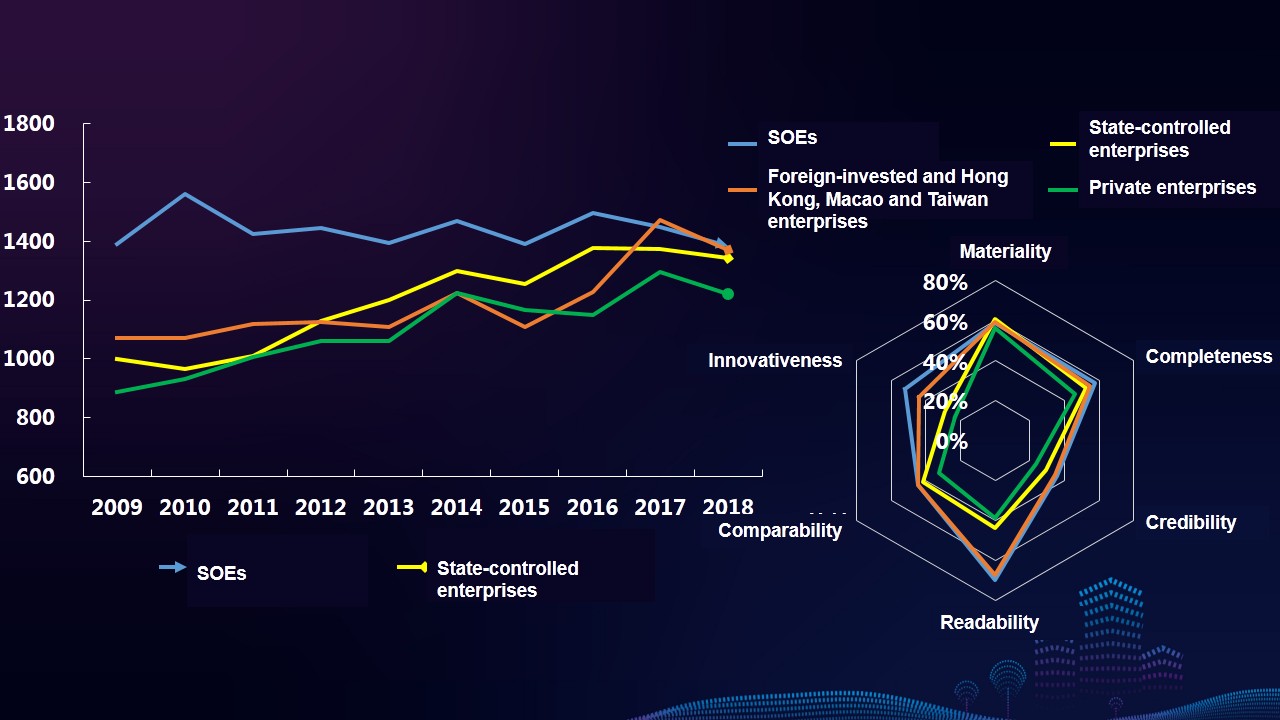
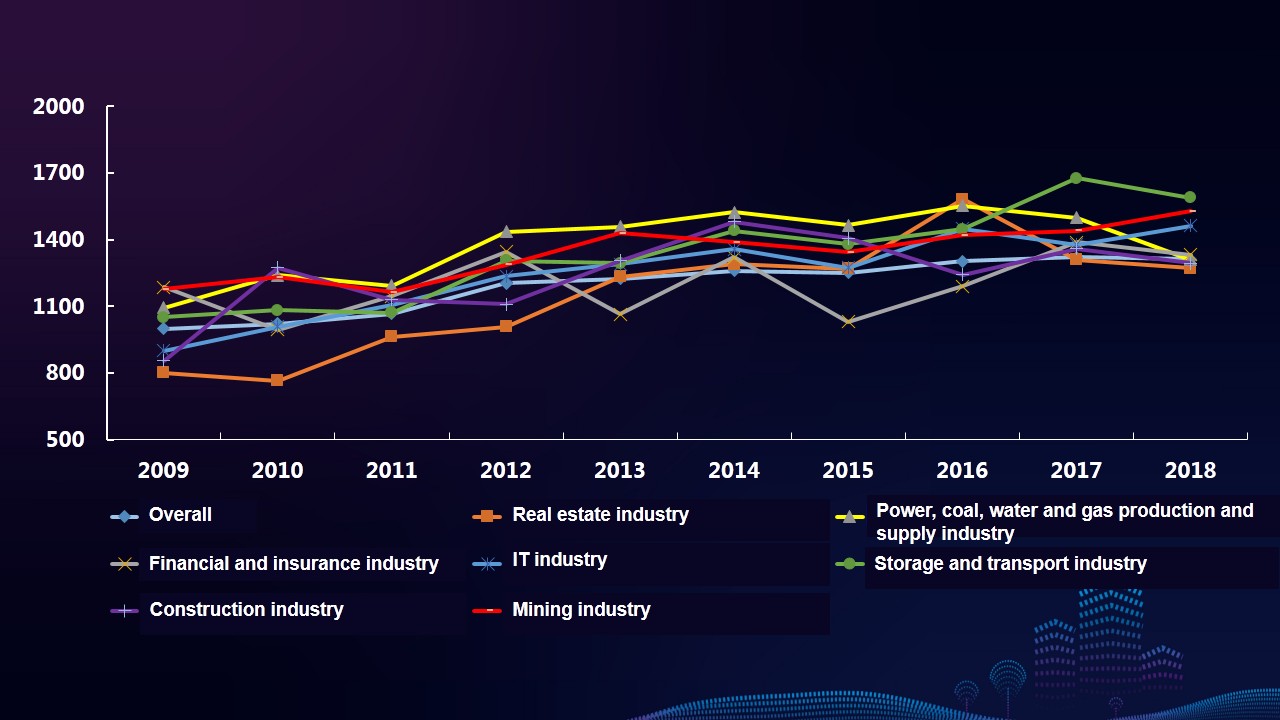
Characteristics 2: The six indexes of CSR reporting all show an uptrend. Compared with the base period, indexes of innovativeness, readability and credibility increase by 480.65%, 156.28% and 60% respectively, and both the indexes of materiality and completeness increase by about 20%. The index of comparability only increases by 2.22%.
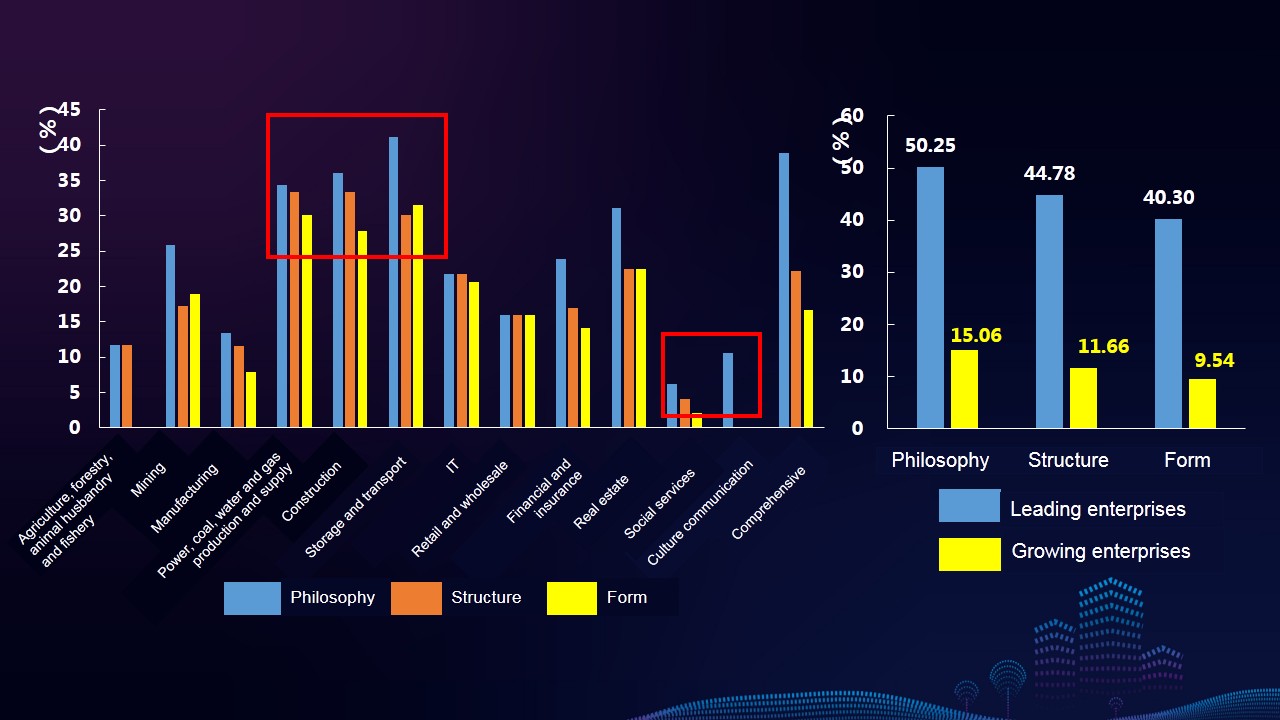
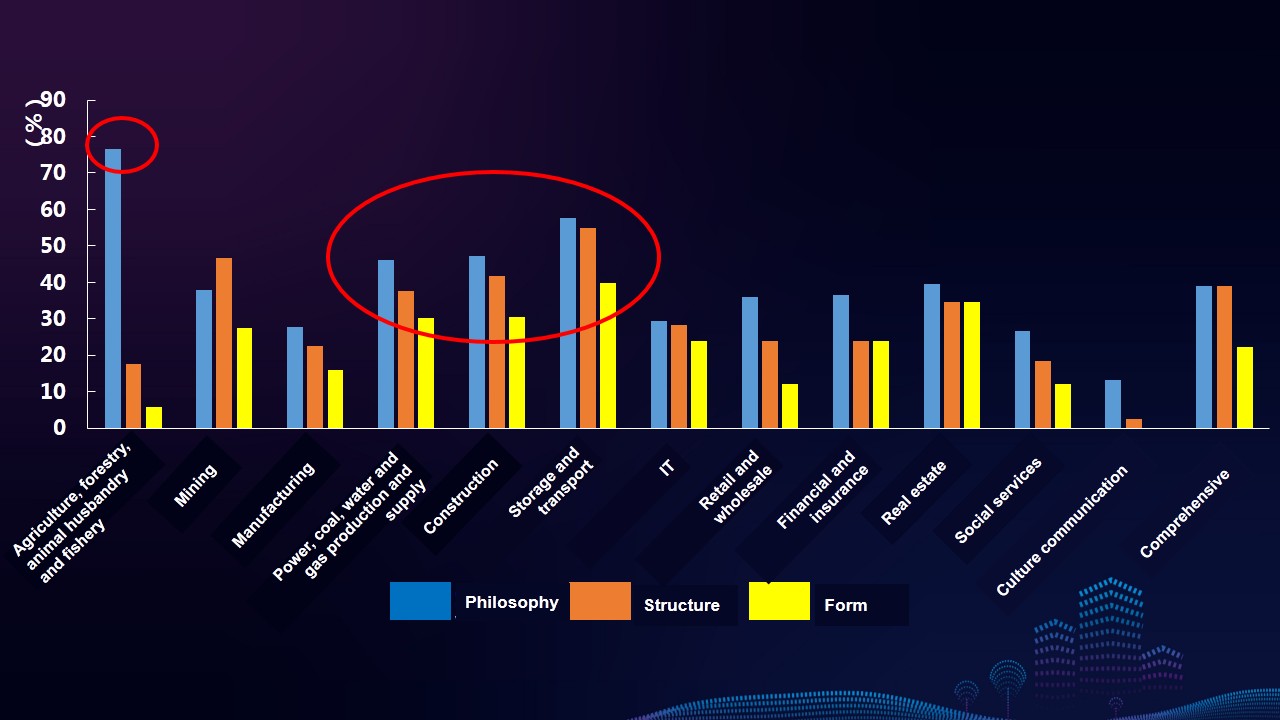
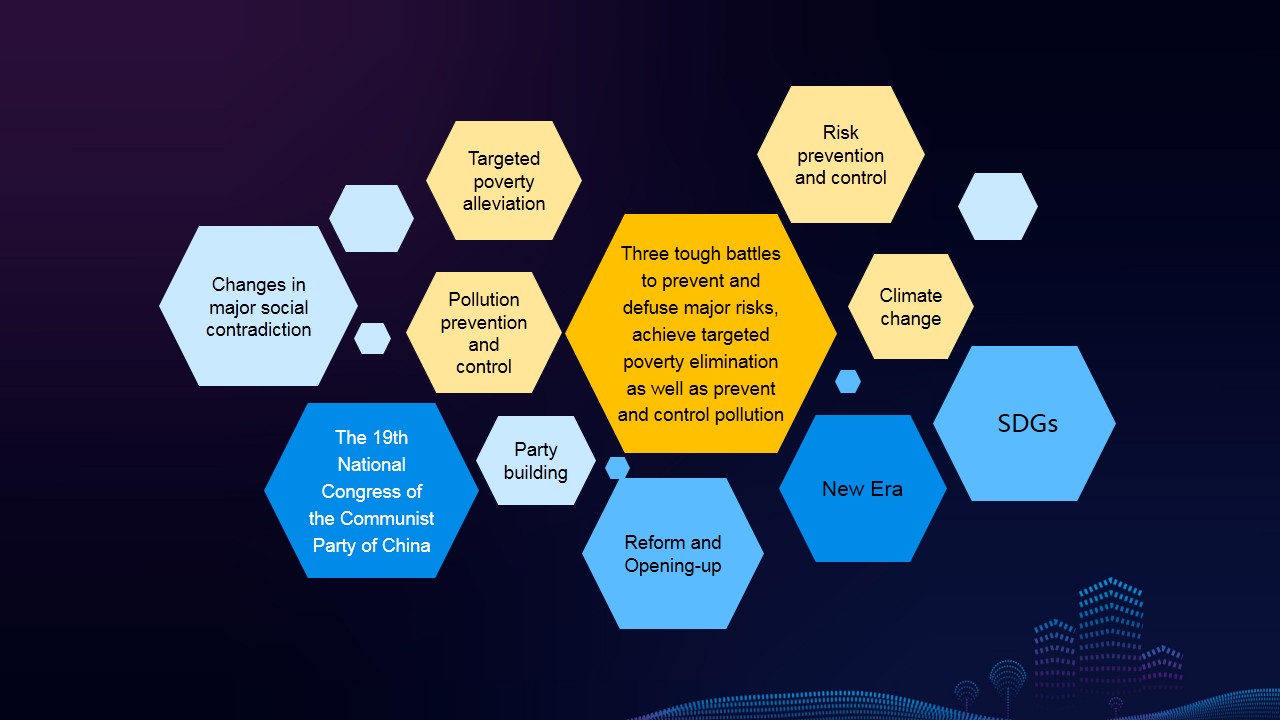
Characteristics 3: Enterprises pay higher attention to information disclosure related to hot issues such as targeted poverty alleviation, pollution prevention and control, and climate change in their reports, reflecting the characteristics of industries and enterprises. Reports released by leading enterprises, as well as enterprises from industries such as power, coal, water and gas production and supply, construction, and storage and transport industry, etc., are more prominent in disclosing the above issues.
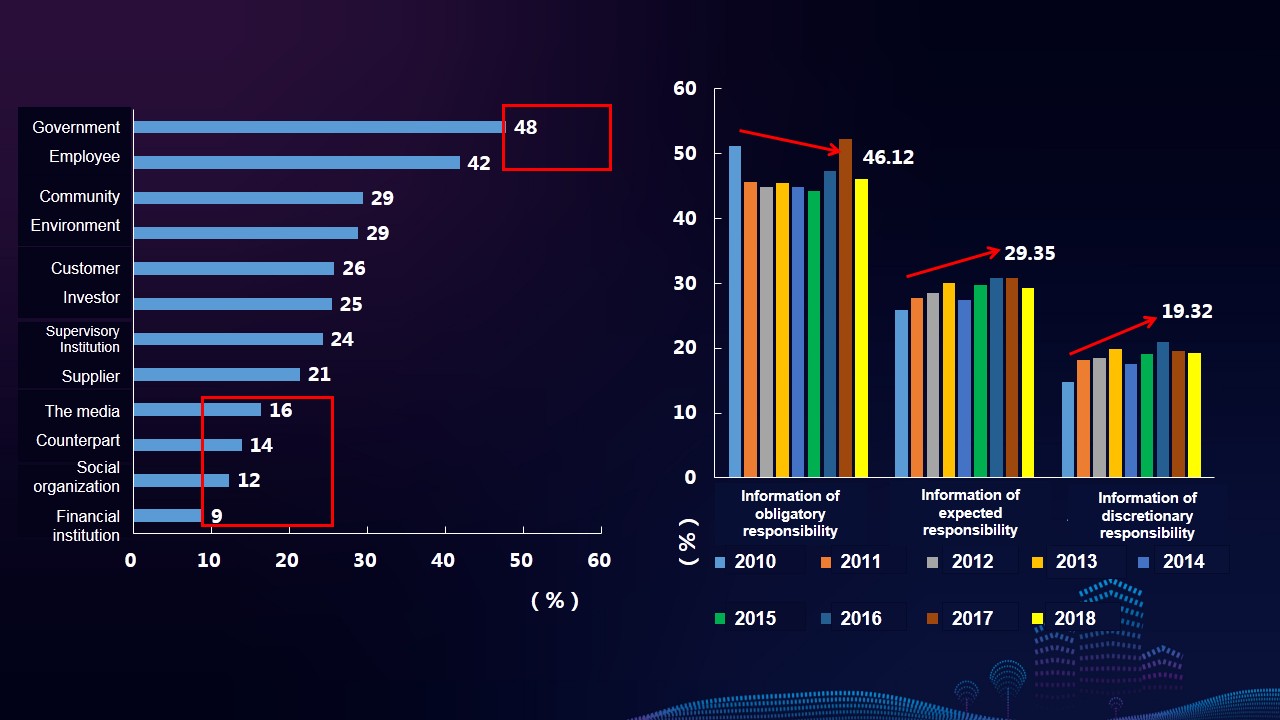
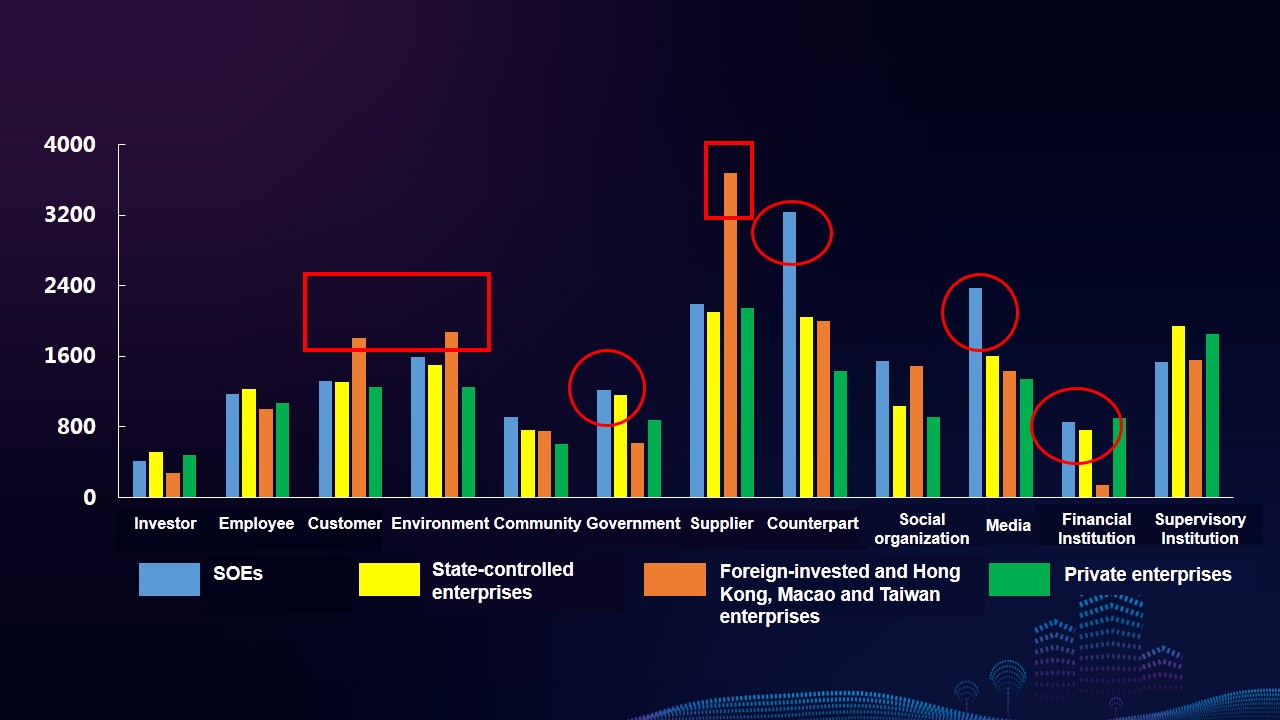
Characteristics 4: The reports have a relatively high degree of information disclosure of responsibility fulfillment of government agencies and employees, while the degree of information disclosure of responsibility fulfillment of the media, counterparts, social organizations and financial institutions is relatively lower. The information disclosure of enterprises’ obligatory responsibility shows a decreasing trend, whereas that of expected responsibility and discretionary responsibility presents an increasing trend.
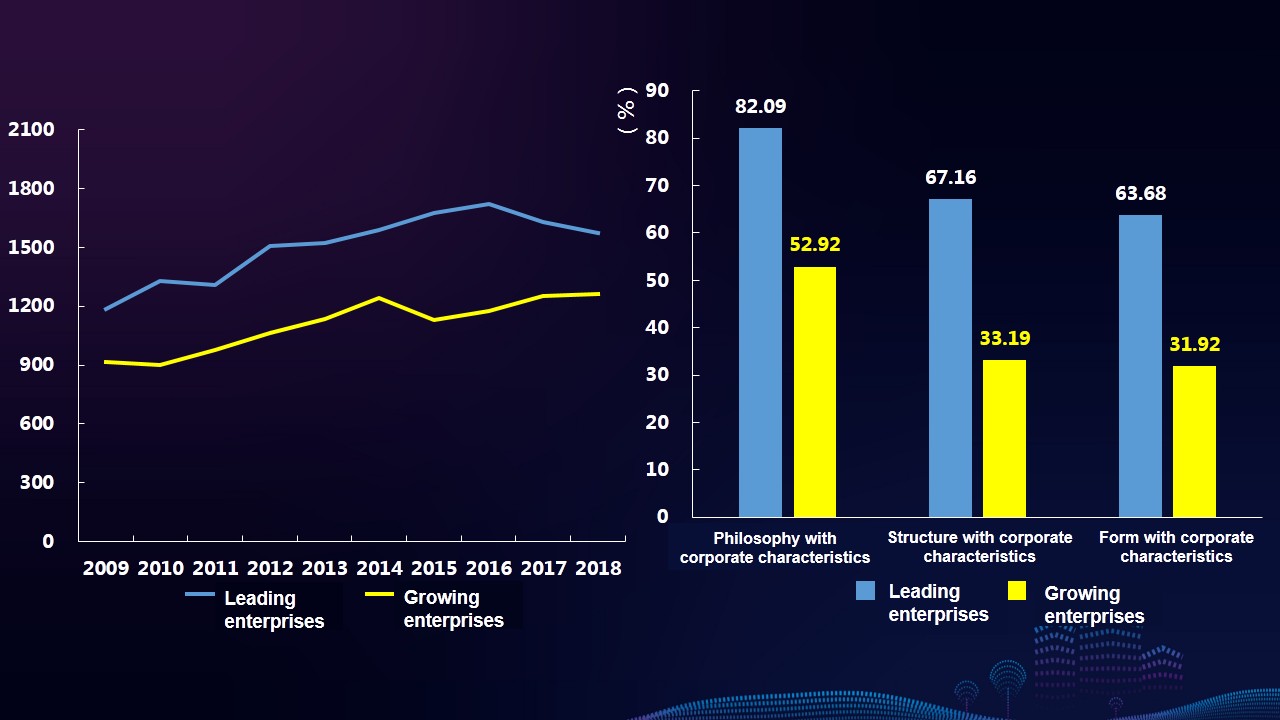
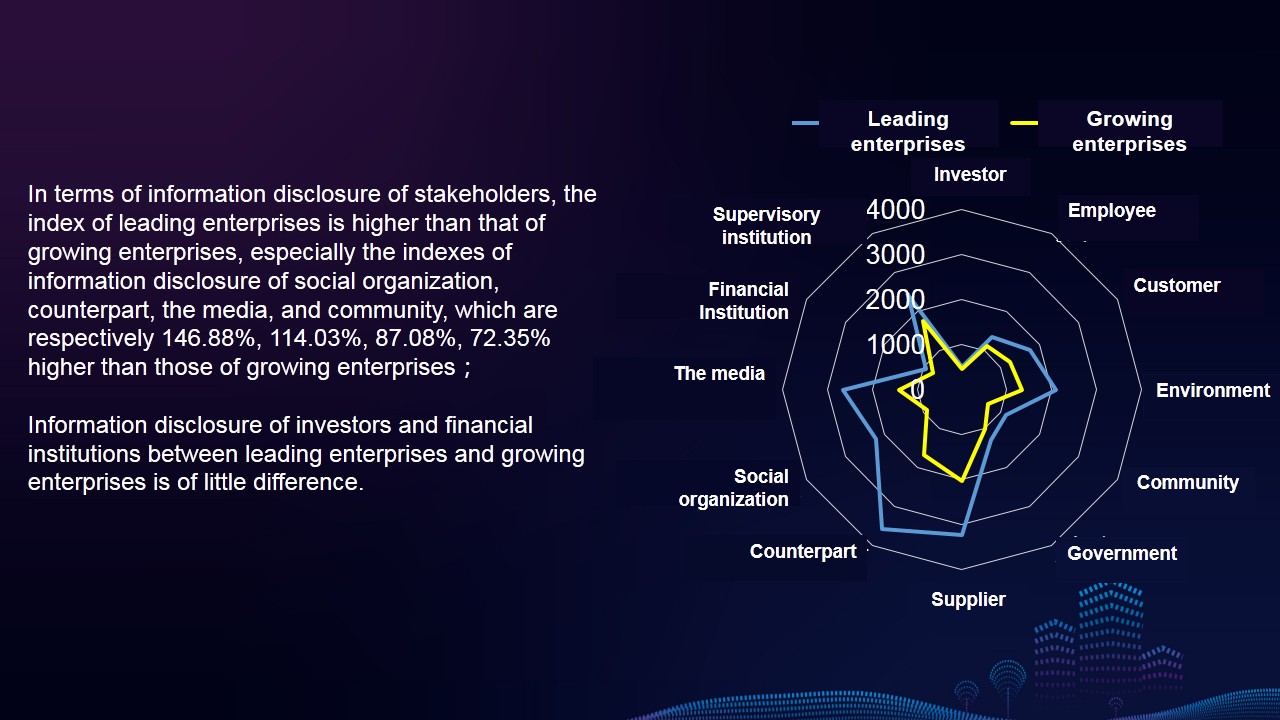
Characteristics 5: The comprehensive index of leading enterprises’ reports is always higher than that of growing enterprises’ reports, but the gap between them has narrowed. Reports of leading enterprises better reflect their corporate strategy, corporate culture, brand image, etc., and they focus more on the information disclosure of stakeholders such as social organization, counterpart, the media, community, etc.
Characteristics 6: The reports of SOEs show a stable development at a high level. The reports quality of state-controlled enterprises, foreign-invested and Hong Kong, Macao and Taiwan enterprises, and private enterprises are catching up, narrowing the gap. Enterprises of different types have different emphases on information disclosure of stakeholders. The reports of SOEs have high index coverage on government and counterpart, and the reports of foreign-invested enterprises are more concerned about suppliers and customers.
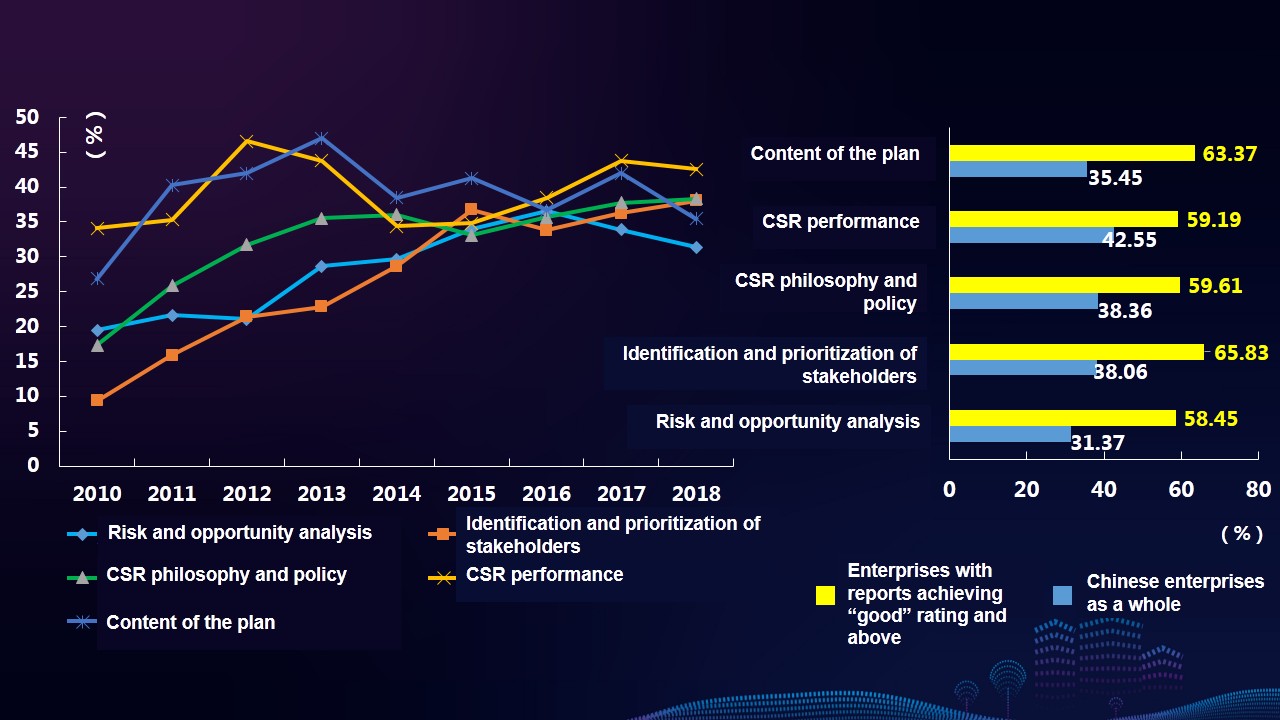
Characteristics 7: The reports focus more on disclosure of management approach of core issues of social responsibility, including the identification and prioritization of issues, risk and opportunity analysis, core issues’ management plans, measures and implementation progress. The reports achieving “good” rating and above and those released by leading enterprises are more prominent in this regard.
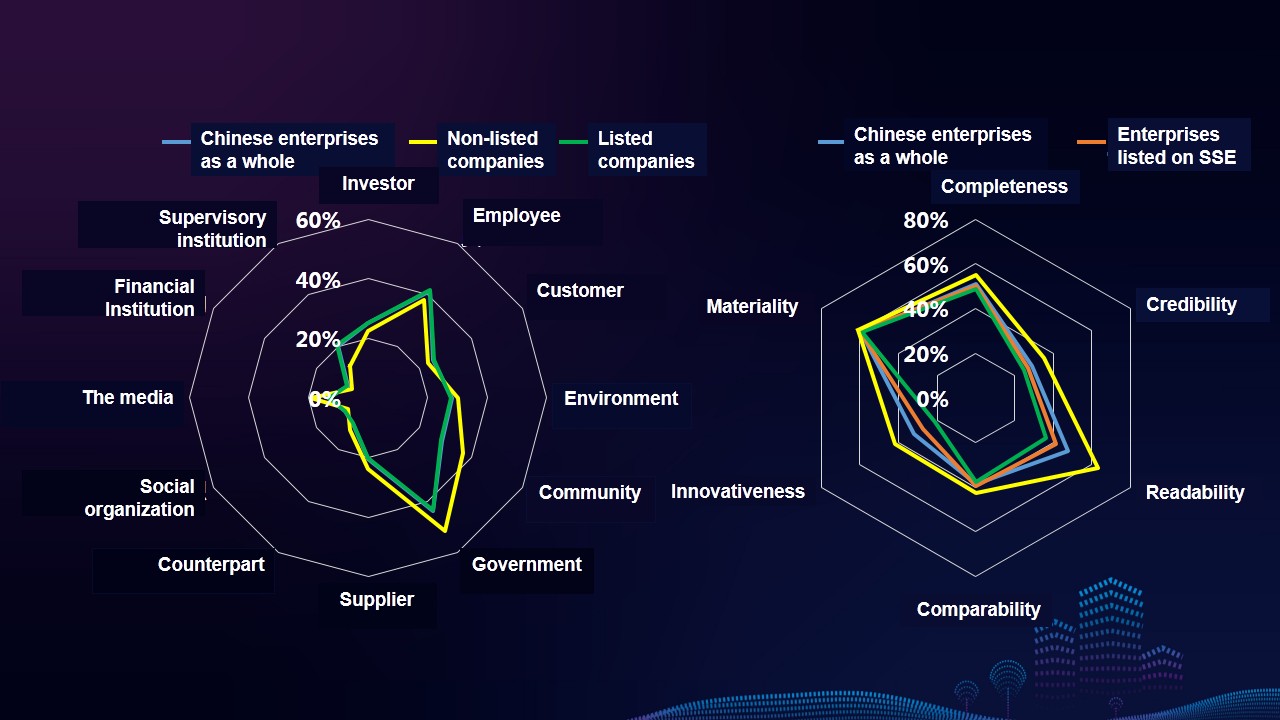
Characteristics 8: Listed companies have higher scores on indicators regarding investor, employee, customer, environment, and supervisory institution. The scores of reports from enterprises in Mainland China listed on Hong Kong Exchanges and Clearing Limited are significantly higher than those of Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) and Shenzhen Stock Exchange as well as the overall level of Chinese enterprises. The information disclosure of customer, environment, community, supplier and counterpart are outstanding.
Characteristics 9: The overall quality of the reports of storage and transport, mining, IT, as well as power, coal, water and gas production and supply industries are relatively high. The comprehensive indexes of mining industry and IT industry increase significantly year on year. Different industries have different focuses on the information disclosure of stakeholders. Industrial characteristics of reports of storage and transport, construction, and power, coal, water and gas production and supply industries are more prominent.
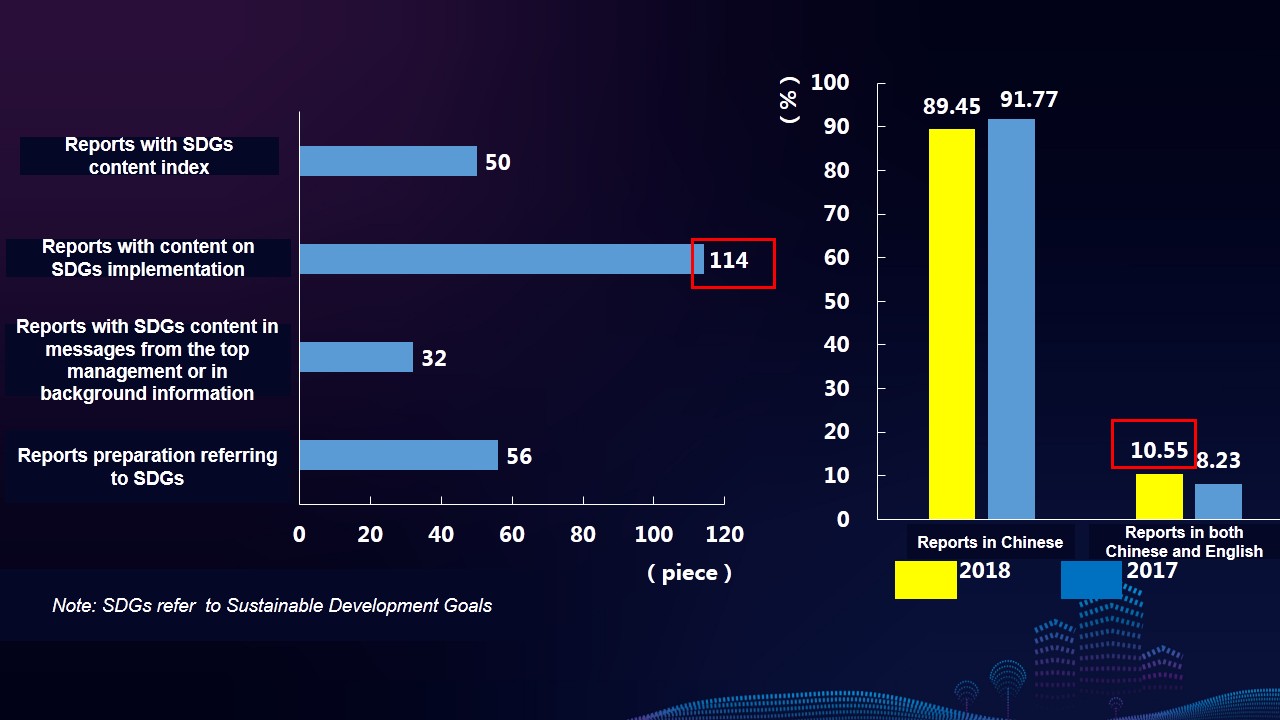
Characteristics 10: The reports lay more emphasis on the information disclosure of responsibility fulfillment overseas, integrate into the international language system, and disclose the information (e.g. localized employment, procurement, community development, etc.) concerned by overseas stakeholders.
Eight suggestions:
Based on the above analysis, eight suggestions are put forward in the Research Report to support enterprises in China to improve their CSR reporting.
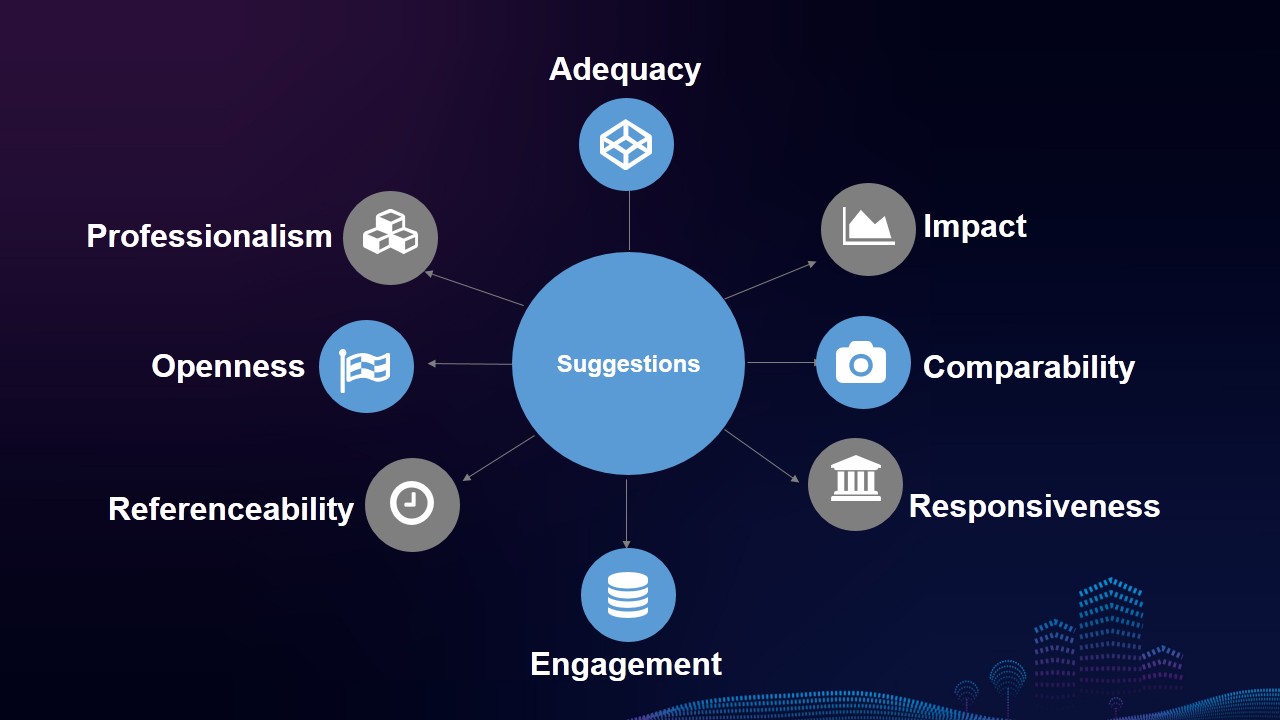
Suggestion 1: Enhance the regulatory role of the government and supervisory institutions on the quality and standardization of CSR reports, and improve the adequacy of CSR information disclosure.
![]()

Suggestion 2: Improve the identification of core issues of social responsibility and the disclosure of management approach of various issues to make the reports truly reflect the impact of information disclosure on sustainable development and stakeholders concerns.

Suggestion 3: Strengthen the disclosure of core performance data of social responsibility, including continuous performance data, intra-industry and cross-industry performance comparisons, to enhance the comparability of reports.

Suggestion 4: Respond to hot sustainability issues in economy, society and environment to enable the CSR reporting to be more responsive to sustainability issues.
Suggestion 5: Improve the credibility of reports, and enhance the engagement of stakeholders in reporting preparation.

Suggestion 6: Strengthen the exchange of CSR reporting among enterprises from different industries and of different types and sizes, and make the reports more referenceable by learning from each other.

Suggestion 7: Actively respond to the Belt and Road Initiative, SDGs, and enhance the application of international reporting standards to increase the reporting openness.

Suggestion 8: Enhance the capability building of staff on CSR reporting in an all-round and multi-level manner according to their actual needs, and improve the professionalism of staff.
